Understanding The Clutch System
Revive Your Ride: Unleash the Power of Our Clutch Repair Expertise!
What is a Clutch?
How does it work?

To gain a better comprehension of clutch problems, it is essential to grasp the functions and operations of a clutch in relation to your vehicle's power-train. The clutch serves as the mechanical component responsible for connecting and disconnecting the power-train or transmission between multiple rotating shafts in a vehicle or any other mechanical apparatus.
The clutch serves as a link between two shafts, enabling them to either rotate together at equal speeds or rotate independently at variable speeds. In automobiles, the clutch is positioned between the engine and the primary driveshaft, regulating the transmission of rotational force and energy from the engine to the wheels. Rotational force, known as torque, is quantified in units such as foot-pounds or newton-metres and represents any force applied at a distance.
Symptoms of clutch pressure plate failure can manifest even when the clutch is not being engaged. When the clutch springs exert force on the pressure plate, they push against the clutch disc. As a result, the clutch disc makes contact with the flywheel, establishing a connection between the engine and the input shaft of the transmission. This connection causes both components to rotate at identical speeds.
Components of the Clutch system.
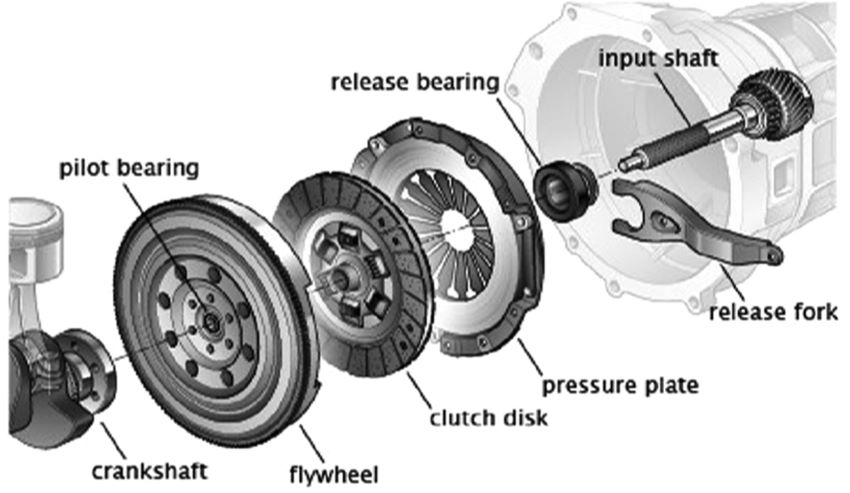
What are the parts of a clutch?
- Clutch disc.
- Release mechanism (either hydraulic or mechanical).
- Cable. - Links the Clutch pedal to the fork.
- Clutch linkage. - Attaches the fork to the Pressure plate.
- Pressure plate. - Attaches to the Clutch disc.
- Flywheel. - Establishes a connection with the engine.
- Pilot Bearing. - Acts as a link between the input shaft and the Clutch disc.
- Clutch release(also known as 'throw-out' bearing).
- Clutch fork. - The linkage controls the force between the pressure plate and the clutch.
A conventional clutch assembly comprises the following elements:
-
Clutch Disc.
This is a circular plate coated with friction material, designed to engage and disengage with the flywheel and pressure plate. With the help of the clutch disc, power is transferred from the engine to the transmission when the clutch is engaged.

-
Clutch Flywheel.
What is clutch flywheel?
What is the function of the flywheel in a clutch?
A heavy, circular component mounted on the engine's crankshaft provides rotational inertia and helps to smooth out engine vibrations. The flywheel also serves as a mounting surface for the clutch assembly.

-
Pressure Plate.
Attached to the flywheel, the pressure plate exerts pressure on the clutch disc when engaged. It uses a set of springs or a diaphragm to exert force, thereby ensuring proper contact between the clutch disc and the flywheel.

-
Clutch Release Bearing.
The release-bearing, as its name implies, is responsible for initiating the disengagement of the clutch when the driver steps on the clutch pedal. It exerts pressure on the pressure plate's release fingers, separating the clutch disc from the flywheel.

-
Clutch Fork.
The clutch fork is responsible for transmitting the driver's input to the clutch release-bearing. When the driver pushes the clutch pedal, it causes the clutch fork to shift, actuating the clutch release-bearing and disengaging the clutch.

-
Pilot Bearing/Bushing.
The pilot bearing or bushing is positioned at the center of the flywheel and has the role of providing support for the transmission's input shaft. It enables the input shaft to rotate freely when the clutch is disengaged and provides alignment when the clutch is engaged.

-
Clutch Alignment Tool.
The clutch alignment tool, used during clutch installation, ensures a proper alignment between the clutch disc, pressure plate, and flywheel. It helps prevent misalignment and facilitates accurate and smooth clutch engagement.
These components work together to enable the driver to engage and disengage the engine's power from the vehicle’s transmission, allowing for the smooth shifting of gears and efficient transfer of torque.
Signs and Symptoms of a Worn-Out Clutch.
How do I know I need a new clutch?
A clutch is an essential component in manual transmission vehicles, as it allows for the smooth engagement and disengagement of power from the engine to the transmission. Over time, due to regular use and wear and tear, the clutch can become worn out and may need replacement. Recognizing the symptoms of a worn-out clutch is crucial in order to address the issue promptly and prevent further damage. In this discussion, we will explore the common signs and symptoms that indicate a worn-out clutch, enabling vehicle owners to identify these symptoms early enough and avert further destruction.
-
Difficulty in Shifting gears.
The clutch is a key component in ensuring smooth gear shifting. If your clutch is worn out, it may not fully engage or disengage, making it difficult to shift gears. In this case, you may need to have the clutch assembly inspected and potentially replaced by a qualified mechanic.
-
Burning smell.
If you detect a scent of burning rubber coming from your vehicle, it could indicate that your car's clutch is overheating, and the Clutch plate is undergoing wear and tear. This issue often arises from excessive use of the clutch in slow-moving traffic conditions.
-
Soft Clutch pedal.
A soft clutch can serve as an initial indication that your clutch is starting to deteriorate. To assess its condition, you should take your car for a brief drive and pay close attention to the sensation and engagement point of the clutch. If you find yourself needing to release the clutch further before the gear engages, it is another sign that the clutch is worn out.
-
Grinding noise when shifting gears.
A grinding noise when shifting gears is often a sign of a worn-out clutch. The clutch plays a vital role in a manual transmission, allowing the driver to connect or disconnect the engine's power from the transmission, which is necessary for changing gears. A worn-out clutch fails to properly engage or disengage, leading to grinding noises during gear changes.
-
Slipping out of gear.
If you experience instances where your clutch disengages from the gear during normal driving, even if it happens infrequently, it is advisable to have it replaced. This occurrence could suggest that your clutch has become worn out or indicate the possibility of an oil leak originating from the crankshaft, which is responsible for lubricating the clutch plate.
-
Higher RPMs.
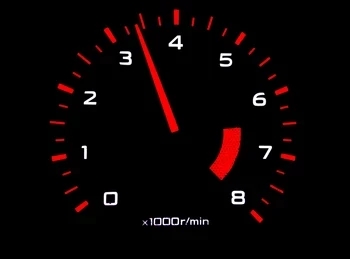
In manual vehicles, the clutch plays a crucial role in the operation of the transmission system, enabling the shifting of gears. When a clutch starts to slip, it means that it is not effectively transmitting power from the engine to the wheels. As a result, the engine's revolutions per minute (RPM) will increase disproportionately as the transmission struggles to function properly.
Causes of Clutch problems(Slipping Clutch).
What causes slipping of the clutch?
- Bent, misaligned or damaged clutch linkage.
- Weakened or warped Pressure plate.
- Worn out or broken motor mounts.
- The clutch assembly is contaminated with either or both engine and transmission oil due to leaking.
- The clutch linkage needs to be adjusted due to constraints on the cable, or rust in the cable housing.
If the clutch fails to disengage correctly, the input shaft will remain in motion, resulting in grinding noises and making it difficult to shift gears in your car.
Some common reasons why a clutch may stick include:
- Disconnected or overstretched clutch cable.
The cable requires the appropriate amount of tension for effective pushing or pulling of the Clutch.
- Leaking, defective, or damaged Slave and Clutch master cylinders.
The clutch master and slave cylinders generate the required amount of pressure for the proper functioning of the Clutch. Leaking cylinders will not be able to generate the required pressure.
- Air in the hydraulic system.
Air interferes with the hydraulic system by occupying the space required by the fluid to generate pressure.
- Misadjusted or Overstretched linkage.
When the clutch pedal is pressed down, the linkage transfers an incorrect amount of force.
- Mismatched Clutch assembly components.
Some aftermarket spare parts may be incompatible with your clutch system.
Signs and Symptoms of a failed Clutch Master Cylinder.

How do you know when your clutch master cylinder is bad?
- Noise from the clutch pedal when shifting gears.
Whistling or whining noises when pressing down the clutch pedal.
- The Clutch pedal chatters or vibrates during acceleration.
- The Clutch disc lining is worn-out due to friction.
- The Clutch disc lining has experienced damage from burning or tainted with oil.
- The Clutch disc might be damaged due to glazing.
- Worn-out splines on the Clutch disc hub.
- Weakened or warped Flywheel or Pressure plate.
- Weakened diaphragm spring of the Pressure plate.
- Hot spots on the pressure plate.
- The Pilot bearing is damaged or worn-out.
- Flywheel is worn-out.
- The clutch pedal sticks on the floor when pressed down.
- Loose or "spongy" Clutch pedal.
- Hard Clutch pedal that is difficult to engage.
- The transmission producing grinding, chirping, or whirling noises while in neutral.
- Grinding noise when engaging and disengaging gears.
- Difficulty in engaging gears in transmission.
Possible causes of a vibrating or chattering Clutch pedal include;
If your clutch release mechanism is hydraulic, and your clutch pedal feels soft or lacks firmness, check for the following:
- The hydraulic line is filled with air.
- Low or no transmission fluid in the reservoir.
- Leaking or damaged pipe.
- Leaking connection.
- The center valve seal in the master cylinder is faulty.
- The primary seal of the piston in the master cylinder is leaking.
Clutch Maintenance Tips.
How do I keep my clutch healthy?
How can I make my manual clutch last longer?
Clutch replacement can be costly and time consuming. Poor handling of the Clutch can lead to it wearing out sooner than expected. Proper driving techniques and regular clutch maintenance is therefore significant in prolonging the lifespan of your clutch, thereby reducing the need of costly clutch replacement.
The way you drive your vehicle plays a crucial role in determining the lifespan of your clutch. By following these guidelines, you can minimize damage and extend the longevity of your clutch to its fullest potential.
- It is important to avoid riding your clutch as it can lead to premature wear and damage. Instead, practice keeping your foot off the clutch whenever you apply pressure to the accelerator.
- Minimize the usage of your clutch to necessary situations. When you come to a stop, shift the car into neutral and release the clutch pedal. Continuously keeping the clutch pedal engaged when it is not required can increase the likelihood of future clutch repairs.
- Avoid using your clutch as a foot rest because it can cause the release of the bearings. Partially engaging the clutch for extended periods can lead to clutch slippage and accelerate wear.
- When driving a manual car, it is not necessary to downshift every time you decelerate. Instead, it is more appropriate to rely on the brakes to slow down the vehicle.
- It is highly beneficial to use your car's parking brake to avoid putting unnecessary strain on the clutch. While leaving the car parked in gear may prevent it from moving, it exerts considerable pressure to the clutch.
- Gentle driving habits: Avoid aggressive driving practices, such as abrupt acceleration, hard braking, and excessive revving. Such habits place additional stress on the clutch and other components, contributing to premature wear and tear.
- Correct gear selection: Ensure that you are in the appropriate gear for your speed and driving conditions. Selecting a gear that is too high or too low can unnecessarily strain the clutch. Familiarize yourself with the recommended shift points for optimal clutch engagement.
- Avoid excessive loads: Do not overload your vehicle beyond its recommended capacity, as this places undue strain on the clutch, transmission, and other parts. Pay attention to the weight restrictions provided by the manufacturer.
- Environmental considerations: Take precautions when driving in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or dusty environments. Excessive heat, cold, or contaminants can affect the performance of the clutch system. Park your vehicle in covered areas whenever possible.
However, even if you employ correct driving techniques, you need to maintain your vehicle properly in order to extend its lifespan. This will also preserve its various components, including the clutch. By adhering to the following practices, you can extend the lifespan of your vehicle:
- Regular servicing: Schedule periodic maintenance and servicing according to the manufacturer's recommendations. This includes oil changes, filter replacements, and inspections of the clutch system. Routine check-ups help identify potential issues early and prevent them from escalating into major problems.
- Fluid checks and replacements: Ensure that all fluids, such as transmission fluid and hydraulic clutch fluid, are at the appropriate levels and in good condition. If necessary, have them flushed and replaced as per the manufacturer's guidelines.
- It is important to pay attention to the sounds your vehicle makes while driving. Make it a habit to drive with the radio off at least once a week so that you can familiarize yourself with the normal noises of your car. By doing so, you will be able to detect any unusual sounds, which can indicate a potential issue with your vehicle. If you notice something out of the ordinary, it is recommended to take your car for a repairs or at least have it inspected by a professional.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can effectively prolong the lifespan of your vehicle, including its clutch, and minimize the likelihood of premature wear and expensive repairs. This will also ensure optimal performance and durability.
Functions of the Clutch
What is the function of clutch?
- Enables smooth gear shifting.
- Works in conjunction with the brakes to reduce the speed or bring the car to stop.
- Transmits torque (rotational force) from the engine to the vehicle's drive train.
- Protect the vehicle's drive train when given inappropriate use.
- Ensure smooth ride by reducing driver related vibrations.
- Smoothly delivers the power generated by the engine to enable the movement of the car.
Types of Clutch systems in vehicles.
What are the different types of clutches?
The market offers a variety of clutch systems, each with its own unique characteristics that set them apart from one another. One way to categorize them is according to the type of discs used, such as hydraulic, single-disc, bi-disc, or multi-disc clutches. Another aspect to consider is the cooling mechanism, which can be either dry or wet clutches. Additionally, clutches can be classified based on the type of control they employ, such as friction, electromagnetic, or hydraulic clutches, among others. Each of these clutch actuators has its unique features and characteristics.
Classification according to discs.
- )
Hydraulic Clutch.
To ensure the proper functioning of a hydraulic clutch, it relies on the activation of hydraulic fluid. Unlike a conventional clutch, the hydraulic clutch does not use discs. Instead, it employs a turbine that derives power from the rotation of the vehicle's engine. However, this type of clutch is not commonly used in regular cars due to its significant fuel consumption and the expensive maintenance required to keep the vehicle in good condition. Nevertheless, it is a clutch system commonly found in industrial vehicles.
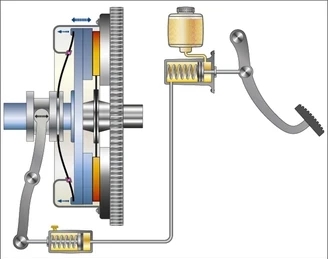
- )
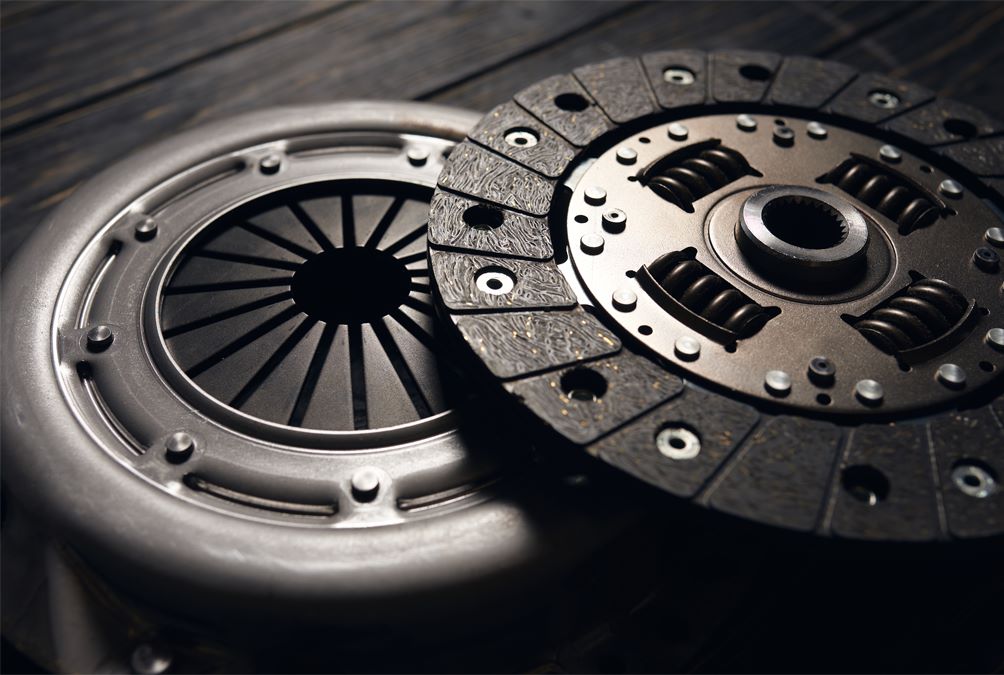
Single-disc Clutch.(Single plate clutch)
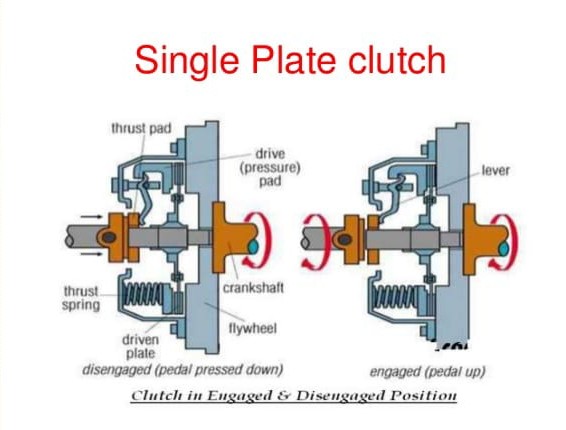
Just as the name suggests, this type of clutch consists of just one disc positioned between the engine flywheel and the pressure plate.
Single plate clutch systems are commonly used in modern light vehicles and play a crucial role in transferring rotational force from the engine to the input shaft of the transmission.
Single plate clutch assembly comprises several essential components, with the clutch plate being a crucial component. The clutch plate connects to the clutch assembly through splines and plays a pivotal role in the overall clutch system. Essentially, the clutch plate can be defined as a slim metal disc with friction surfaces on both of its sides.
The flywheel is linked to the engine's crankshaft and turns together with it. To maintain the clutch in a connected state, the pressure plate is fastened to the flywheel using clutch springs, which exert pressure. When you depress the clutch pedal, the pressure plate has the ability to move along the clutch shaft. Positioned between the flywheel and the pressure plate is a friction plate that does not move. The friction lining is present on both sides of the clutch plate.
- )
Bi-disc Clutch.
This is a type of clutch model that incorporates two discs to effectively transfer the engine's power to the gearbox. It is commonly used in vehicles that generate substantial amounts of power.
- )
Multi-disc Clutch.
This type of clutch system employs multiple sets of plates to establish frictional engagement with the engine's flywheel. This enables the transfer of power from the engine shaft to the transmission shaft in a vehicle. The greater the number of clutches, the larger the frictional surface area available.
As a result, the increased number of friction surfaces enhances the clutch's ability to transfer torque. The clutch plates are installed on both the engine shaft and the transmission shaft.
Multiple clutches function similarly to a single-plate clutch. The assembly comprises plates arranged in an alternating function and connected by coil springs. These plates are enclosed within a cylindrical housing known as a drum. Within this drum, one group of plates moves within grooves located on the flywheel, while the other group move along ridged channels on the pressure plate. This arrangement results in each plate having both an inner and outer spline.
To engage the clutch, one must press the clutch pedal. This action allows the multiple clutches to transmit high torque, making them suitable for heavy commercial vehicles, racing cars, and motorcycles.
Classification according to the type of Cooling.
- )
Dry Clutch.
The clutch system can employ different methods for cooling, and one such method is air cooling, which is favorable for dry clutches.
- )
Wet Clutch.
When oil is used for cooling, it indicates the presence of a wet clutch type.
Classification according to the type of control.
- )
Friction Clutch.
Which is the most common type of clutch?
The most widely used clutch type in cars currently on the road is the friction clutch. It operates by utilizing a flywheel, which is connected to the primary shaft of the gearbox through a bronze bushing. Furthermore, depending on its cooling method, the friction clutch can be cooled using oil.

- )
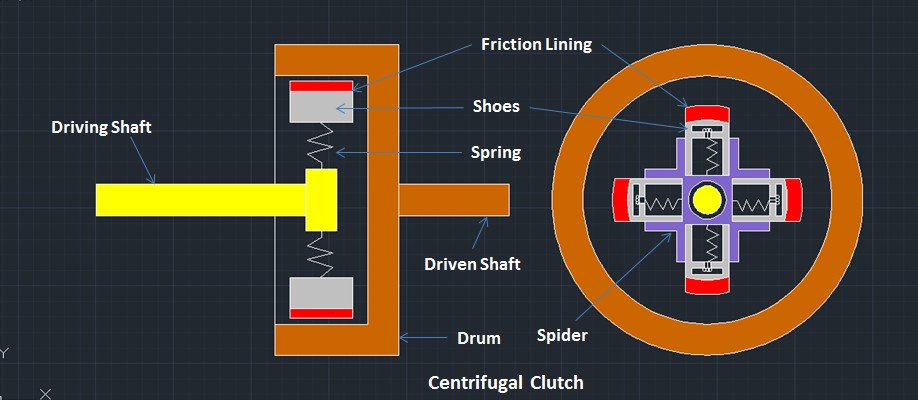
Centrifugal Clutch.
This type of clutch system operates by engaging the engine's torque transmission once it reaches a specific speed. In simpler terms, power is transferred using a centrifugal pump that connects to a turbine, and it is commonly used in various machines like mopeds, lawn mowers, and go-karts to save the engine from stalling when the output shaft comes to an abrupt stop, and to reduce the load during idling and startup. However, more modern technologies, such as fluid couplings and automated manual transmissions, have replaced it in automobile applications because they are better suited for the purpose.
- )
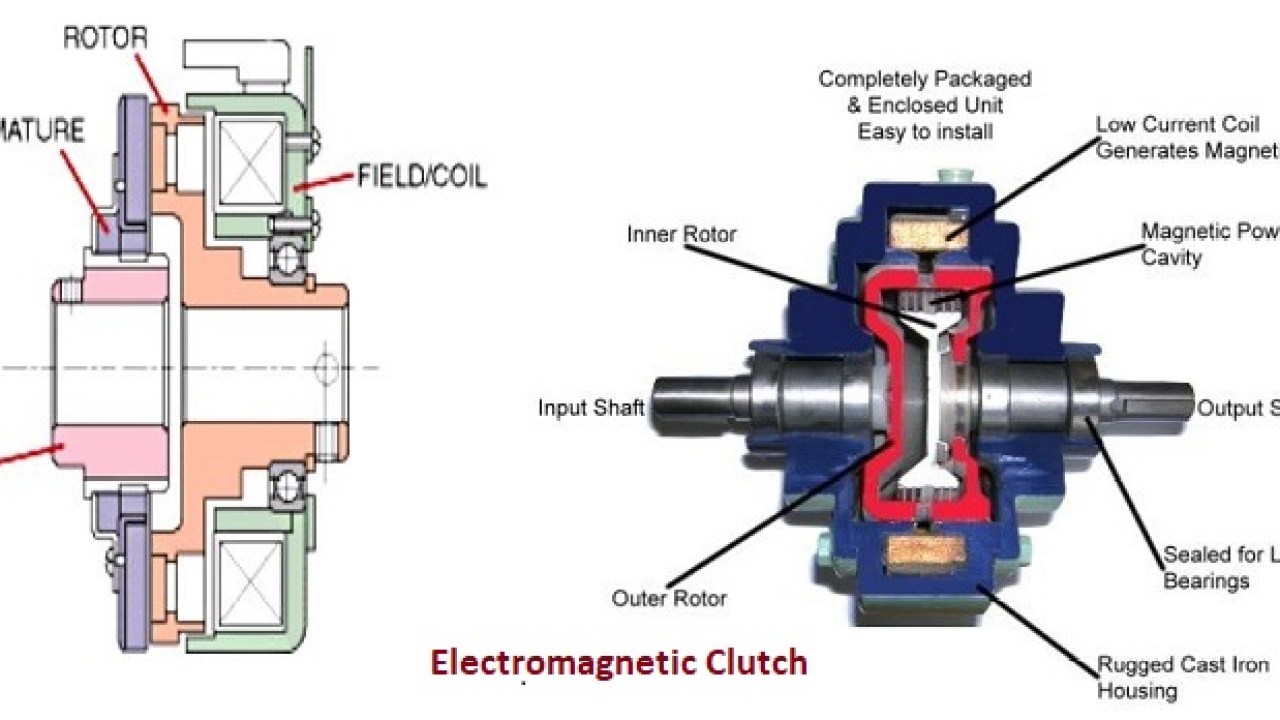
Electromagnetic Clutch.
This type of clutch system, also known as electric power-assisted clutch, operates based on the principle of electromagnetism. It utilizes an iron core and a coil to create an electromagnetic field, which is responsible for transmitting torque.
One key advantage of this type of clutch system is its absence of mechanical linkage for engagement control, resulting in fast and seamless operation. As a result, electromagnetic clutches are highly suitable for remote operations, allowing the clutch to be operated from a distance.
The clutch system in a vehicle relies on an electromagnetic field generated by the winding on the flywheel. This field attracts the pressure plate, engaging the clutch when electricity from the battery passes through the winding. During gear shifting, the clutch release mechanism is activated, interrupting the current flow to the winding and causing the clutch to disengage.
Types of Clutch linkages.
- Cable linkage.
- Shaft and lever linkage.
- Hydraulic-Operator linkage.
In conclusion, promptly addressing clutch problems is important in order to ensure the proper functioning and extended lifespan for the vehicle. The clutch system is vital in transmitting power from the engine to the transmission, and it is essential to promptly address any signs of wear and tear or malfunction. Ignoring clutch problems can lead to further damages to other components of the vehicle and compromise the safety on the road.
Regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential to prevent minor clutch problems from escalating into major and costly damages. No matter the issue, as long as it's a clutch problem, it should be addressed promptly with the help of an experienced mechanic. By identifying and addressing clutch problems early enough, car owners and drivers can not only avoid inconvenient breakdowns but also ensure a smooth and efficient driving experience or ride.